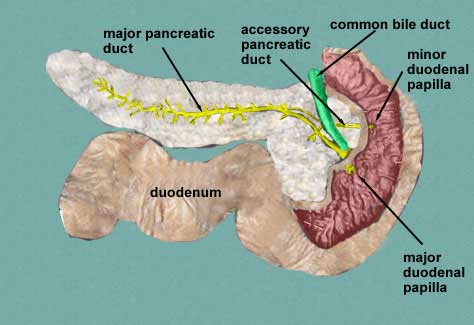
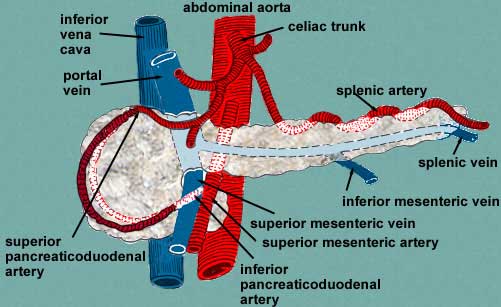
Parts and relations
- Head
- lies within the curve of the duodenum
- uncinate process is a prolongation of the head. The superior
mesenteric artery and vein crosses this process.
- uncinate process
- the part of the head that wraps behind the superior mesenteric artery
and vein and comes to lie adjacent to the ascending part of the duodenum.
- Neck
- a constricted portion to the left of the head. It abuts the pylorus
above and the beginning of the portal vein behind.
- Body
- anterior surface separated from the stomach by the omental bursa
- posteriorly related to the aorta, splenic vein, left kidney
and renal vessels, left suprarenal, origin of superior mesenteric artery
and crura of diaphragm.
- Tail
- extends into the lienorenal ligament and abuts the spleen.
|
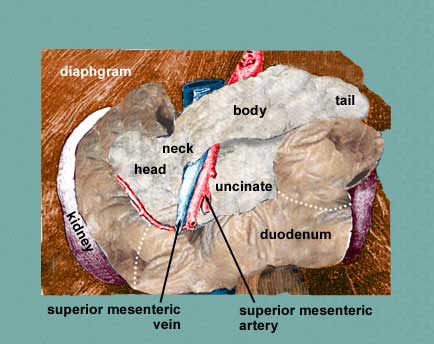
|